VX SIP Configuration page, descriptions and use of fields
Scope
This article adds supplemental information regarding the SIP configuration page on VX Systems
 | VXs style of the SIP Configuration fields |
 | VX, VX Prime, VX Enterprise and Prime Plus style of the SIP Configuration fields |
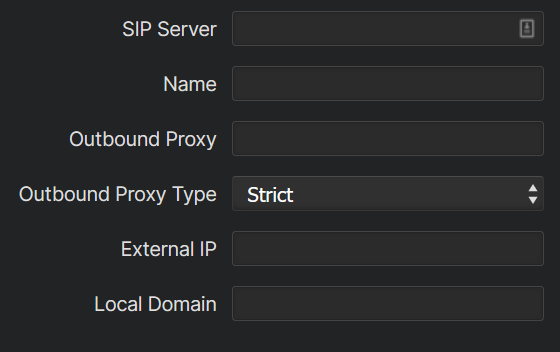
Descriptions and use of fields
SIP Server: The "primary" SIP domain or SIP server address. Used for the domain part in the From headers, Request URI in REGISTER requests, and also for the domain part in the Request URI and To headers in outgoing INVITE requests if it wasn't entered by the user.
Name: Friendly name for the SIP server entry. This name will be shown in the Server drop down when creating Shows
Outbound Proxy: By default, when registering or making an outbound call, the request is sent to server identified by the domain part in the Request URI, resolving it via DNS if it is a domain name. Setting Outbound Proxy lets you override the destination.
Outbound Proxy type: Determines how to format and send the request if Outbound Proxy is set.
There are three possible options:
- Standard - send the request following the rules of the SIP standard (RFC 3261) aka "loose routing" **VXs currently can not set to this and defaults to Fixed which will equal Standard if no Outbound Proxy is set
- Strict - send the request following the old/ outdated standard rules aka "strict routing" (RFC 2543)
- Fixed - send the request to the Outbound Proxy but format the request as if Outbound Proxy was not set.
External IP: The public IP of VX if it is on a private network behind NAT and needs to communicate with the public internet. If set, this will be used in almost every place where VX would otherwise use its own IP address.
Local Domain: The domain of the VX *itself*. When an incoming call arrives, VX looks at the Request URI of the INVITE and matches it with the Request URIs of all lines to find which line it should ring. The matching process includes the domain part of the address. Normally, VX expects to find its own IP address there, because that's what it uses to register the lines. However, in some scenarios where the lines are not registered, the domain part can actually be a domain name. Setting Local Domain tells VX that it should accept calls to that domain.
Let us know how we can help
If you have further questions on this topic or have ideas about improving this document, please contact us.

